|
Junior Member
|
|
Join Date: Sep 2007
Location: Seattle
Posts: 77
|
|
|
Junior Member
Join Date: Sep 2007
Location: Seattle
Posts: 77
|
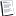
Lewy bodies appear as spherical masses that displace other cell components. There are two morphological types: classical (brain stem) Lewy bodies and cortical Lewy bodies. A classical Lewy body is an eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion that consists of a dense core surrounded by a halo of 10-nm wide radiating fibrils, the primary structural component of which is alpha-synuclein. In contrast, a cortical Lewy body is less well-defined and lacks the halo. Nonetheless, it is still made up of alpha-synuclein fibrils.
(wikipedia)
Lewy bodies have been found in a diverity of locations including monoaminergeic and cholinergic neurons of the brainstem, diencephalon, basal forebrain, cerebral cortex, and autonomic ganglia.
Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Clinical, Pathological, and Treatment Issues By Robert Perry, Ian G. McKeith, Elaine K. Perry. p 288
Enteric malfunction in PD: It was Braak et al. who showed that the first morphological abnormalities such as Lewy bodies and alpha-synuclein deposition do not occur in the substantia nigra, but in the olfactory bulb and in the vagal and glossopharyngeal nuclei. (Braak et al. 2003). The same authors claim that even before this the first Lewy bodies (LB) or a-synuclein inclusions may be found in the enteric nervous system, i.e. gastric, myenteric and submucosal plexuses (also known as Auerbach and Meissner Plexus) (Braak et al. 2005).
(I actually got out a book and typed some of this in. Been a while!)
|