 |
In Remembrance
|
|
Join Date: Sep 2006
Location: about 45 minutes to anywhere!
Posts: 3,086
|
|
|
In Remembrance
Join Date: Sep 2006
Location: about 45 minutes to anywhere!
Posts: 3,086
|
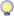 chemical breakdowns in PD
chemical breakdowns in PD
Dopamine biosynthesis
The primary fault in Parkinson's disease is that, whatever the cause, there is insufficient dopamine. Dopamine is formed in the dopaminergic neurons by the following pathway:
L-tyrosine → L-dopa → dopamine
The first step is biosynthesised by the enzyme tyrosine 3-monooxygenase [1.14.16.2] (which is more commonly called by its former name tyrosine hydroxylase). The following is the complete reaction:
L-tyrosine + THFA + O2 + Fe2+ → L-dopa + DHFA + H2O + Fe2+
So for L-dopa formation, L-tyrosine, THFA (tetrahydrofolic acid), and ferrous iron are essential. The activity of this enzyme is often as low as 25% in Parkinson's disease, and in severe cases can be as low as 10%. This indicates that one or more of the elements required for the formation of L-dopa are in insufficient quantities.
The second step in the biosynthesis of dopamine is biosynthesised by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase [4.1.1.28] (which is more commonly called by its former name dopa decarboxylase). The following is the complete reaction:
L-dopa + pyridoxal phosphate → dopamine + pyridoxal phosphate + CO2
So for dopamine biosynthesis from L-dopa, pyridoxal phosphate is essential. The activity of the enzyme rises and falls according to how much pyridoxal phosphate there is. The level of this enzyme in Parkinson's disease can also be around 25% or even far less.
Coenzymes involved in dopamine biosynthesis
Besides two enzymes being required for the formation of dopamine from L-tyrosine (L-tyrosine >>> L-dopa >>> dopamine), three coenzymes are also required. Enzymes are substances that will enable a specific chemical reaction to take place in the body. Coenzymes are substances that assist enzymes. Some enzymes (including those involved in dopamine biosynthesis) will not function without coenzymes.
The three coenzymes involved in the formation of dopamine are : THFA (for L-tyrosine to L-dopa), pyridoxal phosphate (for L-dopa to dopamine), and NADH (for the formation of THFA and Pyridoxal phosphate). They are made from vitamins via the following means :
Folic acid → dihydrofolic acid → tetrahydrofolic acid
Pyridoxine → pyridoxal → pyridoxal 5-phosphate (this requires zinc as a cofactor)
Nicotinamide NMN → NAD → NADH (or NADP) → NADPH
G-proteins
In order to relieve Parkinson's disease, dopamine (or dopamine agonists) must stimulate dopamine receptors, which must in turn stimulate the G proteins :
L-tyrosine → L-dopa → dopamine → dopamine receptors (D2, D3, D4) > G proteins
G proteins consist of three parts : alpha - beta - gamma, that are lined to each other. There are three types of beta unit (1, 2, 4), and seven types of gamma unit (2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 10, 11). However, they do not matter much to Parkinson's Disease. What matters to Parkinson's Disease are the alpha subunits, because it is actually these that ultimately relieve (or aggravate) Parkinson's disease. There are five types:
G proteins that aggravate Parkinson's disease : Gs 1 alpha
G proteins that relieve Parkinson's disease : Gi 1 alpha, Gi 2 alpha, Gi 3 alpha
G proteins that have little effect on Parkinson's disease : Go alpha
The sole purpose of dopamine (or dopamine agonists) stimulating dopamine receptors is to cause the alpha subunits (the active part of G proteins) to break away from the rest of the G protein. Without this occurring almost everybody would have Parkinson's disease. Once the alpha part of G proteins is released, via cyclic AMP, it takes the final action in the series of event that leads to the ridding of Parkinson's Disease, which is to inhibit the cells it has effect on.
Neuromelanin
In the cells involved in Parkinson's disease (the dopaminergic neurons) the function is to produce dopamine. In the melanocytes, which are in the skin, the function is to produce the pigment melanin. Melanin is what causes people to suntan. Although they end up with different substances (dopamine and melanin), both of these cells start off with L-tyrosine, and both of them form L-dopa as well:
dopaminergic neurons : L-tyrosine > L-dopa > dopamine
melanocytes : L-tyrosine > L-dopa > melanin
In the dopaminergic neurons, when somebody can not form dopamine, they can accidentally form melanin instead. In the brain it is called neuromelanin because of the different amino acids it is attached to. However, this is not a normal mechanism, and it occurs via a different mechanism from that found in the skin. The formation of neuromelanin in the brain is often claimed to be what happens in healthy brains. Healthy brains are supposed to be darker in the part of the brain called the substantia nigra. However, it is actually due to the biochemical mechanisms not working properly. As not much L-dopa is formed in Parkinson's disease, there isn't much capacity for that L-dopa to accidentally form melanin in the brain. So people with Parkinson's disease can tend to have not much pigment in the part of the brain called the substantia nigra. However, that does not cause a medical problem because melanin is not supposed to be in the brain.
Cell damage
The primary natural means via which cell damage can occur in Parkinson's disease is due to the reaction from L-tyrosine to L-dopa not taking place. The following is what should happen :
L-tyrosine + THFA + O2 + Fe2+ → L-dopa + DHFA + H2O + Fe2+
However, if for example, the THFA in the above reaction is lacking, the following can happen instead :
L-tyrosine + Fe2+ + O2 → L-tyrosine + Fe3+ + O-2 (superoxide anion)
As can be seen there is no L-dopa formed in the faulty reaction, and the superoxide anion is formed instead. The superoxide anion is one of the most highly destructive elements in cells. The formation of L-dopa can also fail to take place if L-tyrosine is deficient.
So the simplest means of preventing cell damage from taking place is to ensure that you have those substances required for the formation of L-dopa, which are L-tyrosine, THFA (which is made from the vitamin folic acid using nicotinamide), and ferrous iron.
Vitamin C and vitamin E have been used to try to help to prevent cell damage in Parkinson's Disease. This is because they are claimed to assist in two enzyme reactions in the brain that get rid of the superoxide anion once it has been formed :
Superoxide dismutase [1.15.1.1] : 2O-2 + 2H+ → H2O2 + O2
Catalase [1.11.16] : H2O2 → H2O + 1/2 O2
However, the problem with the use of vitamin C and vitamin E in trying to prevent cell damage is that they do nothing at all to prevent the original source of the problem, which is the formation of superoxide anion.
Lewy bodies
Lewy bodies are found in the cytoplasm of neurons. They are often depicted as cellular "rubbish bins" that collect cellular debris. So rather than being the cause of a medical disorder they are a cellular symptom, indicating that cell damage is occurring. They are composed of densely aggregated filaments. These filaments contain ubiquitin and alpha-synuclein. Lewy bodies are often associated with Parkinson's disease. However, they are not unique to Parkinson's disease, as they also occur in several other medical disorders
http://www.goldbamboo.com/topic-t160...s_Disease.html
__________________
with much love,
lou_lou
.
.
by
.
, on Flickr
pd documentary - part 2 and 3
.
.
Resolve to be tender with the young, compassionate with the aged, sympathetic with the striving, and tolerant with the weak and the wrong. Sometime in your life you will have been all of these.
|